
large cash deposits using night safe facilities, thereby avoiding direct contact with bank staff.customers transferring large sums of money to or from overseas locations with instruments for payment in cash and.customers whose deposits contain counterfeit notes or forged instruments.branches that have a great deal more cash transactions than usual (Head Office statistics detect aberrations in cash transactions).
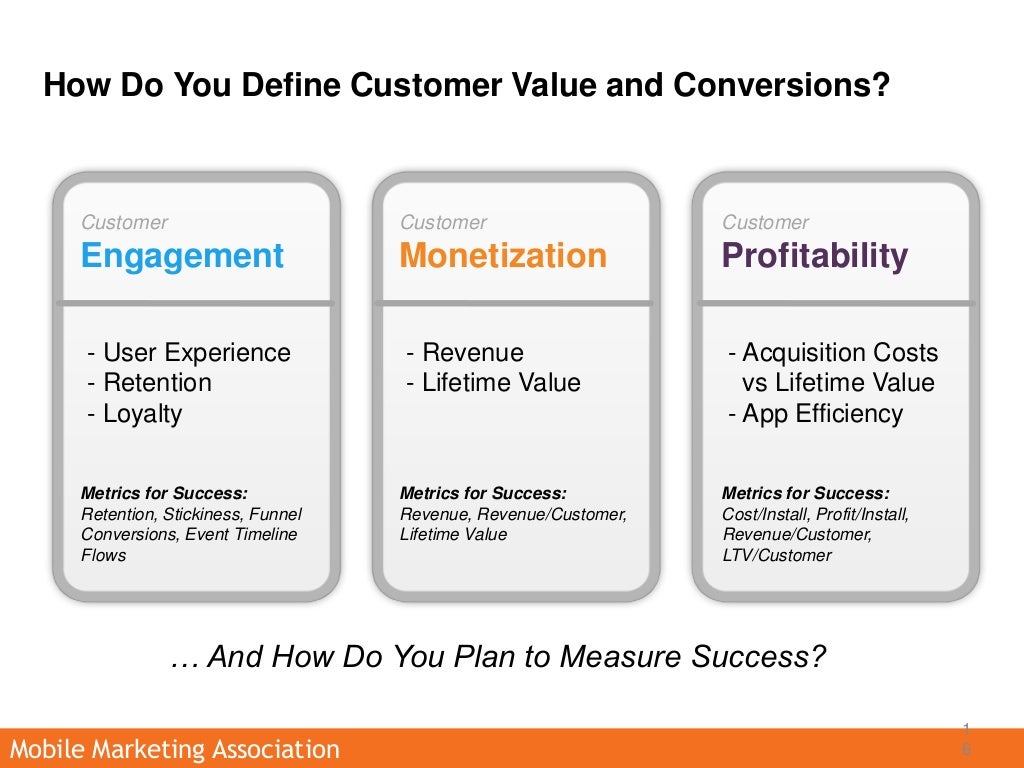
frequent exchange of cash into other currencies.customers who seek to exchange large quantities of low denomination notes for those of higher denomination.customers who constantly pay in or deposit cash to cover requests for money transfers, bankers drafts or other negotiable and readily marketable money instruments.cheques, Letters of Credit, Bills of Exchange, etc.) company accounts whose transactions, both deposits and withdrawals, are denominated by cash rather than the forms of debit and credit normally associated with commercial operations (e.g.customers who deposit cash by means of numerous credit slips so that the total of each deposit is unremarkable, but the total of all the credits is significant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
